Europe, a region steeped in history, has experienced various international conflicts that have shaped its geopolitical landscape. From devastating world wars to regional disputes, these conflicts have had far-reaching consequences and continue to influence the region today. This detailed analysis aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the international conflicts in Europe, exploring their historical origins, key players, and the lasting impact they have had on the continent.
1. Historical Origins
The international conflicts in Europe have their roots in a multitude of historical factors. The two World Wars, sparked by complex alliances, territorial disputes, and rising nationalism, stand as significant events that reshaped the political and social landscape of Europe. Additionally, conflicts such as the breakup of Yugoslavia and the subsequent Balkan Wars, the Irish Troubles, and the more recent conflict in Ukraine are emblematic of the region’s complex historical divisions and unresolved tensions.

2. Key Players
Various actors have played pivotal roles in the international conflicts in Europe:
- European Powers: Throughout history, major European powers, including France, Germany, and the United Kingdom, have been central figures in European conflicts. Their shifting alliances, competing interests, and struggles for dominance have been influential in shaping the outcomes of these conflicts.
- International Organizations: Entities such as the European Union (EU) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) have played significant roles in managing and mitigating conflicts in Europe. The EU has sought to promote economic integration and foster peaceful cooperation among member states, while NATO has focused on ensuring collective defense and security.
- Regional and Ethnic Groups: Europe is home to diverse regional and ethnic groups, some of which have experienced conflicts related to identity, autonomy, and self-determination. Examples include the Basque conflict in Spain, the Chechen conflict in Russia, and the Kurdish struggle for recognition and rights in several countries.
- Global Powers: Superpowers like the United States and Russia have exerted influence in European conflicts. Cold War dynamics, power struggles, and competing geopolitical interests have shaped the involvement of these global players.
3. Impact and Legacy
The international conflicts in Europe have had far-reaching consequences:
- Loss of Life and Displacement: These conflicts have caused immense human suffering, with millions of lives lost and millions more displaced from their homes. The scars of war and conflict continue to affect individuals and communities, leaving a lasting impact on the social fabric of affected regions.
- Political Realignment: European conflicts have prompted significant political realignments and territorial changes. The collapse of empires, the redrawing of borders, and the creation of new states have altered the geopolitical landscape of Europe, with lasting effects on national identities and relationships between nations.
- Economic Disruptions: Conflict disrupts economic stability and development, resulting in significant economic challenges for affected countries and regions. The cost of rebuilding infrastructure, addressing post-war economic disparities, and the diversion of resources towards military expenditures can impede long-term growth and development.
- Social and Cultural Divisions: Conflicts often exacerbate existing social and cultural divisions, deepening rifts between communities and fostering mistrust. Reconciliation and healing in the aftermath of conflicts become critical to building cohesive societies and fostering peaceful coexistence.
- Peacebuilding and Integration Efforts: International organizations, regional initiatives, and grassroots movements have emerged to promote peace, reconciliation, and integration in Europe. Initiatives like the European project, truth and reconciliation processes, and cross-border cooperation aim to foster stability and prevent future conflicts.
The international conflicts in Europe have shaped the region’s history, politics, and identity. Understanding the historical origins, key players, and long-lasting impact of these conflicts is crucial for comprehending Europe’s complex geopolitical landscape. By acknowledging the lessons learned from past conflicts, fostering dialogue and cooperation, and promoting peace-building efforts, Europe can work towards a more peaceful and united future.
4. Lessons Learned and Challenges Ahead
Reflecting on the international conflicts in Europe, several lessons emerge:
- Diplomacy and Dialogue: Diplomatic efforts and dialogue are crucial in preventing and resolving conflicts. Europe has seen successful examples of diplomacy, such as the Good Friday Agreement in Northern Ireland, that offer valuable lessons for resolving complex disputes through peaceful negotiations.
- Multilateralism and Cooperation: International and regional organizations, such as the EU and NATO, play a vital role in promoting peace and stability. Strengthening multilateralism and fostering cooperation among nations are key in preventing conflicts and addressing shared challenges.
- Addressing Root Causes: Understanding and addressing the root causes of conflicts, including historical grievances, social inequalities, and political aspirations, are essential for sustainable peace. Economic development, social justice, and respect for human rights are integral components of preventing and resolving conflicts.
- Media and Information: The media’s role in reporting conflicts is crucial. Journalists have the responsibility to provide accurate, balanced, and objective coverage that promotes understanding and empathy. Combating misinformation and propaganda is vital in preventing the escalation of conflicts.
5. Moving forward, Europe faces on-going challenges in the realm of international conflicts
- Resolving Unresolved Conflicts: Several conflicts in Europe, such as the conflict in Ukraine and the frozen conflicts in Transnistria, Abkhazia, and South Ossetia, remain unresolved. Dedicated efforts, diplomatic negotiations, and inclusive dialogue are necessary to find lasting solutions and foster reconciliation.
- Rise of Populism and Nationalism: The rise of populist movements and nationalist sentiments in some European countries poses challenges to regional integration and cooperation. Addressing the underlying causes of these movements and promoting inclusive societies are crucial for maintaining stability and preventing conflicts.
- Managing Migration and Refugee Crises: Europe has faced significant migration and refugee challenges in recent years, leading to political tensions and societal divisions. Effective management of migration flows, equitable burden-sharing, and integration efforts are necessary to foster social cohesion and prevent conflicts arising from these challenges.
- Hybrid and Cyber Threats: The digital era has brought new forms of conflict, including hybrid warfare and cyber threats. Europe needs to enhance its capabilities to address these non-traditional security challenges, protect critical infrastructure, and strengthen cyber defenses.
The international conflicts in Europe have left a profound impact on the continent, shaping its history, politics, and societies. By drawing lessons from past conflicts, promoting dialogue and cooperation, addressing root causes, and embracing multilateralism, Europe can strive for a more peaceful and integrated future. It is essential for journalists, policymakers, and citizens to work together in fostering understanding, countering misinformation, and building inclusive societies to prevent conflicts and ensure a prosperous and harmonious Europe.
6. Comprehensive understanding of media coverage in European conflicts
Europe, a region marked by diverse histories and geopolitical complexities, has witnessed numerous conflicts that have garnered global attention. Aspiring journalists, it is crucial to explore the nuances of media coverage in international conflicts in Europe. This student-friendly and engaging section aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of media coverage in European conflicts, incorporating abstracts from a journalism point of view and promoting critical thinking and ethical reporting.
- Understanding European Conflicts: Europe’s history is intertwined with conflicts that have shaped the continent’s political landscape. These conflicts have diverse origins, including territorial disputes, ethnic tensions, economic disparities, and ideological differences. Understanding the historical context of each conflict is crucial for accurate reporting.
- Challenges in Reporting on European Conflicts: Journalists reporting on European conflicts face several challenges. Language barriers, cultural nuances, and differences in media landscapes across countries can complicate the collection and interpretation of information. Journalists must navigate diverse perspectives, biases, and the potential politicization of conflicts to provide balanced and accurate reporting.
From a journalism perspective, reporting on European conflicts requires adherence to ethical principles and responsible reporting practices. Journalists should strive for accuracy, fairness, and impartiality. Verifying information through multiple reliable sources and fact-checking are crucial in countering misinformation and propaganda that often accompany conflicts.
Journalists should be aware of their own biases and strive to present diverse perspectives. Recognizing the complexities of conflicts in Europe, journalists must aim to provide context and analysis to foster a comprehensive understanding among their audiences.
7. Ethical Considerations
Ethics play a vital role in reporting on European conflicts. Journalists must prioritize the safety and well-being of individuals involved in the conflict, including sources and subjects. Sensitivity to the cultural, historical, and political dimensions of the conflict is essential in producing ethical and responsible reporting.
Additionally, journalists should exercise sensitivity to the cultural, historical, and political dimensions of the conflict. Cultural awareness and respect for local customs and traditions are paramount to ensure accurate and respectful reporting. Journalists should avoid perpetuating stereotypes or reinforcing biases, striving instead for balanced and nuanced coverage.
8. Promoting Accuracy and Context
In reporting on European conflicts, journalists should aim for accuracy and context. The complex nature of these conflicts demands in-depth research, interviews with key stakeholders, and an understanding of historical events. Providing accurate and comprehensive information is vital to promote understanding and foster dialogue.
9. Engaging Diverse Perspectives
Reporting on European conflicts necessitates amplifying diverse perspectives. Journalists should seek out voices from different sides of the conflict, including representatives from conflicting parties, civil society organizations, and local communities affected by the conflict. This approach encourages a more nuanced and balanced portrayal of the conflict.
10. The Power of Storytelling
Storytelling is a powerful tool in reporting on European conflicts. By humanizing the conflict through personal stories, journalists can elicit empathy and create a deeper understanding among their audience. It is crucial to maintain sensitivity and respect for the individuals whose stories are shared, protecting their privacy and ensuring their safety.
Media coverage of international conflicts in Europe carries immense responsibility. Journalism students must navigate the challenges of reporting on diverse European conflicts while upholding ethical principles. By embracing critical thinking, seeking diverse perspectives, and providing accurate and balanced reporting, they can contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of European conflicts.
Responsible reporting not only informs the public but also helps promote understanding, empathy, and dialogue. Journalism students have the power to shed light on the complexities of European conflicts, challenge stereotypes, and contribute to a more peaceful and inclusive world. By engaging in informed and ethical reporting, they can shape public discourse and inspire positive change.
11. Historical Context of European Conflicts
Europe has a rich history of conflicts, shaped by a complex tapestry of historical events, cultural differences, and political dynamics. These conflicts range from the World Wars to the breakup of Yugoslavia, the Northern Ireland Troubles, and more recent conflicts such as the Ukraine crisis. Understanding the historical context of each conflict is crucial for journalists reporting on them, as it provides valuable insights into the root causes, grievances, and dynamics at play.
12. Challenges of Reporting on European Conflicts
- Journalists reporting on European conflicts face a range of challenges. Language barriers can make it difficult to gather accurate information and interview key sources, particularly in regions with diverse linguistic backgrounds. Cultural nuances and historical sensitivities require journalists to have a deep understanding of the local context and dynamics to accurately convey the complexities of the conflict.
- Another challenge is the potential politicization of conflicts. Journalists must navigate biases, propaganda, and disinformation campaigns that may be employed by different parties involved in the conflict. It is essential for journalists to remain vigilant, fact-check claims, and present a balanced account of events to counteract potential biases.
- From a journalism perspective, reporting on European conflicts demands adherence to ethical standards and responsible reporting practices. Journalists should prioritize accuracy and factual integrity, ensuring that information is verified and corroborated through multiple reliable sources. This is particularly important in conflicts where competing narratives and misinformation are prevalent.
- Journalists should be aware of their own biases and strive to present diverse perspectives. Balancing conflicting viewpoints can provide audiences with a more nuanced understanding of the complexities inherent in European conflicts. It is crucial to avoid sensationalism and instead provide comprehensive analysis and context to foster a deeper understanding among readers.
13. Promoting Accuracy, Context, and Accountability
In reporting on European conflicts, journalists should prioritize accuracy and provide essential context. Historical background, political dynamics, and the impact of the conflict on the lives of people must be conveyed to create a comprehensive understanding among readers. Journalists should also hold all parties accountable for their actions, providing thorough investigations into human rights abuses, war crimes, and other violations of international law.
14. Engaging Diverse Perspectives and Humanizing the Conflict
Journalists should seek out and amplify diverse perspectives in their coverage of European conflicts. This includes providing a platform for voices from conflicting parties, civil society organizations, and local communities affected by the conflict. By presenting the human stories behind the conflicts, journalists can evoke empathy and foster a greater understanding among their audience.
Media coverage of international conflicts in Europe is a challenging but essential task for journalists. Reporting on these conflicts requires a deep understanding of the historical context, cultural nuances, and political dynamics at play. By upholding ethical principles, promoting accuracy, providing context, and amplifying diverse perspectives, journalism students can contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of European conflicts. Responsible reporting fosters empathy, challenges biases, and plays a crucial role in shaping public discourse and promoting peace and reconciliation.
ERITREA-ETHIOPIA BORDER CONFLICT (CASES STUDY)
While media coverage often focuses on conflicts, it is essential to acknowledge instances where media played a significant, albeit underrated, role in resolving international conflicts. One such example is the role of media in helping to solve the Eritrea-Ethiopia border conflict. The conflict, which lasted for decades and resulted in a devastating war, was finally brought to an end through a combination of diplomatic efforts and the influential role of the media in fostering peace.
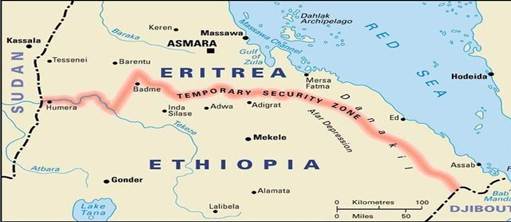
1. Background
The Eritrea-Ethiopia border conflict dates back to the late 20th century when Eritrea sought independence from Ethiopia. Following a long and bloody war, Eritrea gained independence in 1993. However, disputes over border territories remained, leading to sporadic clashes and tensions between the two nations.
2. The Role of Media in Conflict Resolution
Media coverage brought attention to the Eritrea-Ethiopia conflict, particularly during periods of heightened violence. Journalists reported on the human toll, displacement of communities, and the devastating consequences of the conflict. This raised awareness among the international community and put pressure on both nations to seek a resolution.
3. International Diplomatic Pressure
Media coverage played a crucial role in mobilizing international diplomatic efforts to resolve the conflict. News reports shed light on the human rights abuses, displacement, and humanitarian crises resulting from the conflict, prompting international organizations and countries to take action. The media acted as a catalyst, pushing for diplomatic negotiations and dialogue between the two nations.
4. Peacebuilding Narratives
Media outlets played a significant role in shaping peace-building narratives and fostering dialogue between Eritrea and Ethiopia. Journalists highlighted stories of reconciliation, peace initiatives, and shared cultural heritage between the two nations. By emphasizing commonalities and promoting empathy, the media contributed to creating an environment conducive to peaceful resolution.
5. Public Opinion
Media coverage influenced public opinion both domestically and internationally. As the conflict received increased media attention, public sentiment began to shift, urging governments to prioritize peace. Within Eritrea and Ethiopia, media outlets provided platforms for peace activists, intellectuals, and civil society groups to voice their concerns and advocate for a peaceful resolution.
6. Track II Diplomacy
Media platforms facilitated “Track II Diplomacy,” which involved unofficial negotiations and dialogues between individuals, organizations, and intellectuals from both nations. By providing a space for discussions and promoting alternative viewpoints, the media helped build bridges and fostered mutual understanding and trust.
The underrated role of media in resolving the Eritrea-Ethiopia border conflict showcases the significant impact media can have in international conflict resolution. Through raising awareness, mobilizing international diplomatic pressure, shaping peacebuilding narratives, influencing public opinion, and facilitating Track II Diplomacy, the media played a vital role in bringing the conflict to an end.
This example highlights the power of the media as a force for positive change and peacebuilding. It underscores the importance of responsible journalism, accurate reporting, and the media’s ability to shape public discourse. By recognizing and highlighting such instances, we can appreciate the potential of the media in resolving conflicts, fostering dialogue, and building a more peaceful world.



