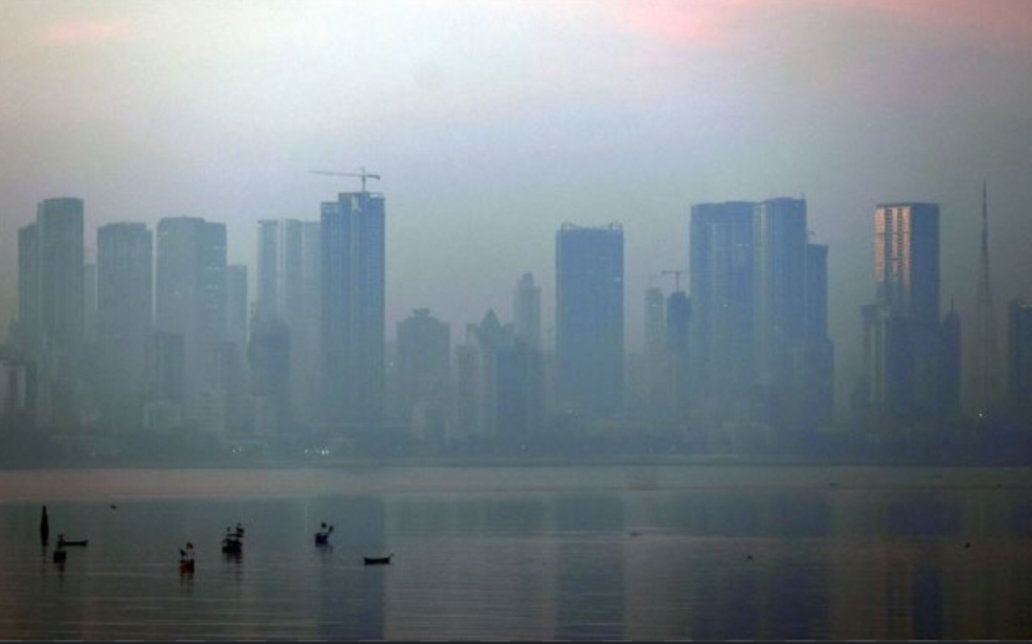
Mumbai is facing an environmental crisis due to increasing air pollution levels. This has been caused by a combination of factors, including rapid industrialization, a surge in the number of vehicles on the roads, and inefficient waste management.
The Air Quality Index (AQI) of Mumbai is currently at an unhealthy level, with PM2.5 and PM10 particulates at 92 µg/m³ and 223 µg/m³ respectively. This can have serious health implications, particularly for those who are sensitive to air pollution, and has been linked to a range of respiratory and cardiovascular issues.

Furthermore, the AQI levels in the residential area of Sector-19A Nerul, Navi Mumbai, are even higher, with a PM10 particulate level at 102 µg/m³, and an O3 AQI at 32. This indicates that air quality in the region is deteriorating rapidly, and that more needs to be done to mitigate the problem.
The government should make it a priority to reduce air pollution in Mumbai, for the sake of the health of its citizens.
The financial capital of India, Mumbai, is now competing with the national capital, Delhi, for the title of having the worst air quality. Traffic emissions, construction operations, paved and unpaved road dust, landfills, open rubbish burning, and industrial emissions are the major causes of air pollution in Mumbai. Road and construction dust is the major source of pollution in Mumbai, contributing to 29% of the PM (Particulate Matter) present in the air.

Power generation plants are the biggest contributors to air pollution in Mumbai, followed by heavy-duty vehicles running on diesel. Deforestation and air quality awareness are also factors that contribute to the deteriorating air quality in the city. Solutions to the air pollution problem include boosting mass public transport, reducing deforestation, and improving air quality awareness.
Air pollution in the city of Mumbai has been a serious issue for many decades now. According to a report from the Ministry of Environment and Forest (MOEF), Mumbai recorded the highest number of deaths due to air pollution in 2018. The report states that about 11,000 people died due to air pollution in Mumbai in 2018, which accounts for nearly 20% of all air pollution deaths in the country.

The number of deaths now has increased to 13,444 in Mumbai, due to a number of factors such as an increase in vehicular emissions, industrial emissions, and the burning of biomass. The city also faces an alarming level of air pollution due to construction activities and open burning.
The air pollution has been linked to serious respiratory and cardiovascular health issues, prompting authorities to take steps to mitigate the problem. The government has implemented measures like tightening emission norms and promoting public transport, but more needs to be done.
It is clear that much more needs to be done to reduce air pollution in Mumbai. To tackle this issue effectively, the government needs to focus on reducing vehicular emissions, industrial emissions, and open burning, and should also promote the use of cleaner fuels and energy sources. Additionally, the government should encourage citizens to adopt greener lifestyles, and should enforce strict regulations to limit air pollution.