According to recent UN data, India has surpassed China to become the world’s most populous nation, with a population of 1.4286 billion people compared to China’s 1.4257 billion. India’s population has grown by over one billion since 1950, while China’s population is decreasing due to low birth rates and an aging workforce.
The UN predicts that India’s population will surpass 1.5 billion people by the end of the decade and peak at 1.7 billion people in 2064. Factors influencing population growth include fertility rates, increasing longevity, and international migration.
India has become populous country in the world, with a population of over 1.4 billion people. While the country’s large population has provided several opportunities for growth and development, it has also led to several negative consequences, including poverty, environmental degradation, and social unrest.

One of the biggest challenges posed by overpopulation is the strain it places on the country’s resources. With limited land, water, and energy resources available, the increasing demand from a growing population has led to depletion and degradation of natural resources. This has contributed to environmental degradation, such as deforestation, soil erosion, air and water pollution, and loss of biodiversity.
The impact of overpopulation is particularly severe in urban areas, where the population is concentrated. Cities are struggling to provide basic services such as housing, sanitation, and transportation to the growing population. The lack of adequate infrastructure has led to overcrowding, slums, and poor living conditions, which can contribute to health problems and social unrest.
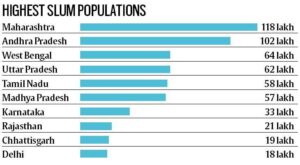
Overpopulation has also led to widespread poverty and inequality in India. The country has a large population of people living in poverty, with limited access to basic services such as healthcare, education, and sanitation. This can contribute to a cycle of poverty, as individuals struggle to break out of the cycle due to a lack of opportunities and resources.
The government of India has recognized the challenge of overpopulation and has taken steps to address it. The country has implemented several programs to promote family planning and provide access to contraception, as well as initiatives to promote sustainable development practices. However, the scale of the challenge remains daunting, and much work remains to be done to address the negative effects of overpopulation in India.


