The Five Product Levels identified by Philip Kotler
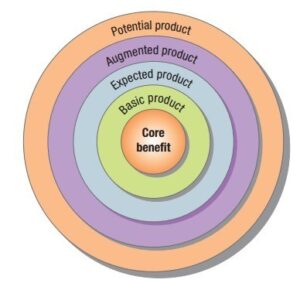
The product levels, or product hierarchy, provide a holistic viewpoint on the many elements of a product that customers engage with. Philip Kotler, a marketing professor, first proposed these levels, which consist of five fundamental components:
- Core benefit
At the core benefit level, a company identifies the essential value or main objective that a customer desires when buying a product. This feature specifically targets the fundamental requirement or issue that the product is intended to solve.
For instance, when someone purchases a smartphone, they are primarily seeking the fundamental advantage of communication and immediate access to information.
- Generic Product
Transitioning to the generic product level encompasses the fundamental iteration of the product that effectively delivers the primary advantage. This level encompasses all the fundamental characteristics and qualities required for the product to fully operate as intended. Fundamentally, it is a collection of concrete and abstract characteristics that constitute the product.
In the context of smartphones, these components would include but are not limited to the display, processor, battery, and fundamental communication capabilities.
- Expected product
The expected product level refers to the defined characteristics and qualities that consumers expect to be present in a product belonging to a certain category. The following are the essential criteria that consumers anticipate while engaging in a purchase. If these anticipated characteristics are not met, it may result in customer discontent.
For instance, when it comes to smartphones, consumers would anticipate attributes such as a high-resolution camera, full compatibility with applications, and reliable internet access.
- Augmented product
Upon reaching the augmented product stage, we come across supplementary features and advantages that exceed customers’ expectations and set the product apart from its rivals. These additional features enhance the value and greatly improve the entire client experience. Enhancements to product offers may encompass warranties, customer assistance, packaging, post-purchase services, or loyalty schemes.
As an example, in the context of smartphones, augmented features may encompass an extended warranty, rapid charging technology, or restricted access to specific applications.
- Potential Product
Finally, the potential product level involves imagining future possibilities and technological advancements that could be included into the product. These are concepts and enhancements that may not be presently accessible but possess the inherent capacity to be implemented in the future. Successfully predicting and adjusting to evolving client demands and technical progress are essential elements of the prospective product level.
As an example, in the case of smartphones, the prospective product could include a gaming kit on one instance and earbuds on another instance. Through prospective products, a company might astonish its clients.