Introduction
The media is an important factor in determining public perception and understanding of political parties and personalities in India. As future journalists, it is important to recognize the influence of media in political coverage and the responsibilities that come with it. This section investigates the various aspects of media’s role in covering political parties and personalities in India, highlighting prominent and recent examples from a journalism standpoint.

1. The Watchdog Function
Journalism serves as a watchdog, holding politicians and political parties accountable for their actions. Media outlets investigate and report on the policies, statements, and activities of political parties and personalities, ensuring transparency and informing the public. For example, when a political leader makes controversial remarks, the media plays a crucial role in exposing and analyzing their impact, fostering public discourse and shaping public opinion.
- The Mughal emperor was referred to by the Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister, who was speaking at a rally in Sambhal district, as “Babur ki aulad (Babur’s descendant).” The comment on the Samajawadi Party candidate while making light of the 72-hour suspension the Election Commission had placed on him for making a communally insensitive remark.
- The ‘Chowkidar chor hai’ comment by Rahul Gandhi to Narendra Modi had boiled up the situation.
2. Election Coverage and Political Campaigns
During election seasons, the media plays a significant role in providing information and analysis to voters. Journalists cover political campaigns, organizing debates and interviews to help citizens make informed decisions. For instance, televised debates between political leaders allow the public to compare their ideologies, plans, and credibility, assisting voters in understanding different perspectives and making educated choices.
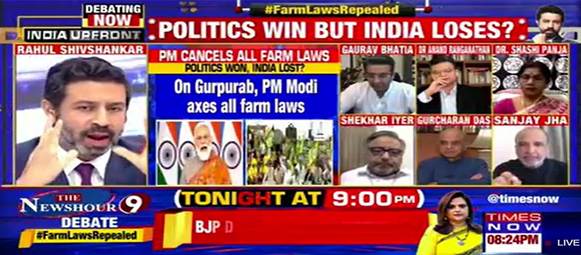
3. Agenda Setting and Framing
Media outlets play a pivotal role in agenda setting, determining which political issues receive extensive coverage. By emphasizing certain topics or controversies, the media can influence public perception and shape political discourse. For example, by focusing on issues like unemployment, farmers’ protests, or healthcare, the media can shape the public’s understanding of the political landscape and the priorities of political parties.

4. Political Bias
Journalists must strive to maintain objectivity and balance in their reporting. However, biases can unintentionally seep into news coverage, affecting how political parties and personalities are portrayed. It is crucial for journalists to remain vigilant and ensure fair representation of different viewpoints. For instance, some media outlets have been accused of favoring or targeting specific political parties, which can influence public opinion and undermine the democratic process.
5. Influence on Public Opinion
Media coverage of political parties and personalities can significantly impact public opinion. Journalists have the power to shape the narrative surrounding political figures, influencing how they are perceived by the public. For instance, positive or negative coverage can impact a political party’s popularity and electoral success. The media’s responsibility lies in providing accurate, balanced, and unbiased coverage, allowing citizens to form their own opinions based on reliable information.
There are some noticeable examples given below:
1. 2014 Indian General Elections
The media extensively covered the electoral campaigns of various political parties, including the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and the Indian National Congress (INC). The media played a crucial role in highlighting key issues and facilitating discussions that influenced public opinion and voting patterns.
2. Prime Minister Narendra Modi
The media’s coverage of Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been extensive and diverse. While some media outlets have praised his policies and initiatives, others have scrutinized his governance. This wide-ranging coverage has influenced public opinion about his leadership and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP).
3. Regional Political Parties
Media coverage of regional political parties, such as the Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) in Delhi or the All India Trinamool Congress (TMC) in West Bengal, has influenced their popularity and electoral success. The media’s portrayal of their leaders and policies has shaped public opinion and affected voter behavior.
As aspiring journalists, understanding the media’s role in covering political parties and personalities in India is essential. The media acts as a watchdog, provides election coverage, shapes public opinion, and influences the political discourse. However, it is imperative for journalists to maintain objectivity, avoid biased reporting, and ensure fair representation of different political parties and personalities. By adhering to ethical journalism practices, journalists can contribute to a well-informed electorate and a healthy democracy.
It is important to recognize that the media’s role in covering political parties and personalities is not without challenges and controversies. Media organizations face pressure from various stakeholders, including political parties, advertisers, and even the audience, which can sometimes compromise the integrity of their coverage. Journalists must remain vigilant, uphold journalistic principles, and prioritize the public interest above all else.
In conclusion, the media plays a significant role in the coverage of political parties and personalities in India. Through their watchdog function, election coverage, agenda setting, and influence on public opinion, journalists shape the political landscape and facilitate democratic participation. It is crucial for aspiring journalists to understand these dynamics and commit themselves to ethical and responsible journalism, ensuring that the media remains a powerful force for informed decision-making and a robust democracy.


