(Photo-Magzter)
India is the most populous country in the world, with a high number of youth and middle-aged people residing there. Being over populated also makes it an employment-demanding country. Since the last 50 decades, our world has seen a total of five different revolutions. All revolutions that have passed have brought some or other changes in work, jobs, and employments, along with a change in the hierarchy of organisations.
Right now, the whole world is jumping from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0. The world is in the process of going to the next industrial revolution, which is the industrial revolution of human-robot collaborations, customizations, and cognitive systems, basically where both humans and robots are working together.
All five different industrial revolutions over time are:
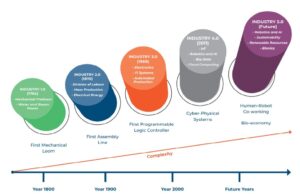
Industry 1.0: In this industrial revolution, the focus was on the items being produced by the machines, which were working on water and steam. This industrial revolution came around 1780.
Industry 2.0: This was the second industrial revolution, where in the industrial processes that were done by the machines, those machines were working with the help of electrical energy. It was also responsible for the mass and bulk production taking place at that time. This industrial revolution is also known as technological revolution, which only occurred in Germany, Britain, and America. It came around the 1870s.
Industry 3.0: Being the third in line, this industrial revolution brought automation and automated production with the help of robots, electronics, and computers. It came around the 1970s.
Industry 4.0: In this industrial revolution, the focus is heavily on interconnectivity, machine-learning, the Internet of Things, cyber-physical systems, AI, data analytics, and automation. This industrial revolution came in 2000.
Industry 5.0: The upcoming industrial revolution, which focuses on the interaction of humans and robots together, human-robot collaborations, or working together. It brings out how robots help humans work faster with the help of advanced technologies. This came in 2020.
When we talk about Industry 5.0, it has its advantages as well as its disadvantages. The main advantage of Industry 5.0 is the creation of higher value jobs, which helps in brilliant personalization for customers and freedom in design creativity. It allows the manufacturing processes to be done by automation, so that the human workers are focused on delivering improved, bespoke products and services on time.

Industry 5.0 has technologies that are very smart, connected machines with customised software, machine learning, and industrial automation that would be able to forecast production efficiency based on recent activities. This industrial revolution is also pushing companies more and more towards sustainability and resilience as it assures the wise use of resources, which would later make businesses more flexible and agile. Human-robot collaboration will create flexible business models that will eventually reduce waste and overproduction.
One of the main disadvantages of Industry 5.0 is that it will be very expensive. One-on-one training people for jobs and buying technologies will not be cheap. Some way or another, big companies may find a way to overcome the upgrade of their production, but small companies will not be able to afford it all. Some companies and organisations would not be able to adapt to the change and accept the new concept altogether.
Machines and robots do make life easier, but humans also need to do things on their own. They need to develop some new skills, including how to collaborate with a machine. A person who has great technical skills will be needed. So, learning and developing new skills is very important.
India has a very high number of low-paying jobs and a very smaller number of high-paying in the formal sector. The low-paying jobs in India have no social security, whereas more than 80 percent of the Indian working population works in the informal sector. India is aspiring to become a manufacturing hub. Various initiatives such as Make in India, Skill India and Start-up India are helping in achieving this aim. In its recent report, the National Association of Software and Services Companies (NASSCOM) mentioned that the Indian manufacturing industry has spent between $5.5 to $6.5 billion on Industry 4.0 solutions in 2020-21.
The Indian government has set a target of increasing the contribution of manufacturing output to 25% of GDP by 2025. The integration of Make in India with the principles of Industry 4.0 can help in achieving the desired objectives and can eventually make India the forerunner in smart manufacturing systems.