A. Evolution of Advertising
Introduction
We know it when we see it. We are exposed to it thousands of times every day. Most of us are reasonably proficient, although rarely perfect, at distinguishing it from other kinds of messages. But what is this thing called advertising?
In other words, advertising is the act of calling public attention to an idea, product, or service through paid announcements by an identified sponsor. But there’s more to advertising. An average human is exposed to around thousands of advertising messages in a day. Advertisements come in many different ways, like shapes, sizes, colors, patterns, and forms.
Definition
According to Philip Kotler, “Advertising is any paid form of non-personal presentation and promotion of goods, services, or ideas by an identified sponsor.”
According to Frank Presbrey, “Advertising is a printed, written, oral, and illustrated art of selling. Its objective is to encourage sales of the advertiser’s products and to create in the minds of people, individually or collectively, an impression in favor of the advertiser’s interest.”
According to Wheeler, “Advertising is any form of paid non-personal presentation of ideas, goods, and services for the purpose of inducing people to buy.”
The mediums used are print, broadcast, and direct.
According to William Stanton, “Advertising consists of all activities involved in presenting to a group a non-personal, oral or visual, openly sponsored, identified message regarding a product, service, or idea. The message, called an advertisement, is disseminated through one or more media and is paid for by the identified sponsor.”
A. Evolution of Advertising
Advertisements have come a long way in the past century or so. As it’s had to adapt and change to suit new mediums and audiences constantly. To raise the value of the advertising of today and imagine the advertising of tomorrow, we need to comprehend the origin and evolution of advertising.
Advertising was produced by a market-driven system and developed in a capitalistic, free enterprise market economy in which mass production utilized advertising as an essential tool. Urbanization, transportation expansion, and communication advancements all facilitated the use and growth of advertising, the result of which is that advertising is firmly entrenched as a business function in different societies with deeply rooted economic and cultural foundations.
Advertising is the result of years of development in capitalism and its use in mass communication media. We can define advertising as a form of commercial mass communication designed to promote the sale of a product or service or a message on behalf of an institution, organization, or candidate for political office. That implies concepts such as market, publics, sponsors, persuasion, products, services, mass communication, etc.
1. The Beginning
In the Middle Ages, together with street callers, brands appeared on products for identifying the maker, giving them a sign of individuality from a manufacturer from others, allowing for differentiation, for example, between wines and geographical areas such as Osnabruck and Westphalia.
In this period, a big number of people can’t read. So, signs that today would say “cobbler,” “miller,” “tailor,” or “blacksmith” would use an image associated with their trade, such as a boot, a suit, a hat, a clock, a diamond, a horseshoe, a candle, or even a bag of flour.
Gutenberg’s printing press (1438) really began the era of mass communication in that now printed materials could be mass-produced, whereas prior to the printing press, books and other printed materials had to be made individually. A Londoner printed the first English newspaper in 1622, and the first ad appeared in 1625.
That 1622’s first newspaper was the Weekly News, by Nicholas Brown and Thomas Archer. Other newspapers of this time were the Mercurius Britannicus, in 1665, and La Gazzette from Paris by Théophraste Renaudot in 1630. Those were considered beginners of modern advertising, despite the fact that the first newspaper announcement appeared in 1650 in the Several Proceedings in Parliament; it was about offering a reward for returning twelve stolen horses.
2. Propaganda and Mechanization
Today, the word ‘propaganda’ carries a negative and harmful connotation.
During World War I, advertising became a medium for propaganda. Governments used advertising to convince their citizens to join the military. This period also saw increased mechanization of the industry, making ads more costly.



a. Why do the war perpetrators use propaganda?
- Each of the nations that participated in World War One from 1914 to 1918 used propaganda posters.
- They used posters to:
- Justify their involvement to their own population
- As a means of recruiting men
- A way to raise money and resources to sustain the military campaign.
- To urge conservation



b. Why Posters?
- Television had not yet been invented
- Not everyone owned or had access to a radio
- Posters were the most effective means of getting a message across





3. The Emergence of New Media
The major media types or groups that have been introduced since the beginning of the twentieth century include film, sound recordings, radio, television, personal computers, videocassettes, video games, and the Internet. During this time, new mass media, radio, and cinema became commercially available in the first part of the 20th century; the advertising industry quickly took advantage of their reach, spread, and popularity.
New media are forms of media that are native to computers, computational, and rely on computers for redistribution. Some examples of new media are telephones, computers, virtual worlds, single media, website games, human-computer interfaces, computer animation, and interactive computer installations.
New media are often contrasted to “old media,” such as television, radio, and print media, although scholars in communication and media studies have criticized rigid distinctions based on oldness and novelty. New media does not include television programs (only analogue broadcast), feature films, magazines, or books, unless they contain technologies that enable digital generative or interactive processes.
Wikipedia, an online encyclopaedia, is a good example of new media, combining Internet-accessible digital text, images, and video with web links; creative participation of contributors; interactive feedback of users; and formation of a participant community of editors and donors for the benefit of non-community readers.
Facebook is another type of new media, belonging to the category of social media model, in which most users are also participants. Another type of new media is Twitter, which also belongs to the social media category, through which users interact with one another and make announcements that the public receives. Both Facebook and Twitter have risen in usage recently and have become an online resource for acquiring information.
4. The Creative Advertising Revolution
At that time there was not a great deal of competition for an advertising message. Television was just beginning; people had time to read. But it was clear to us that there would soon be tremendous competition for the attention of the consumer. And that unless the advertising message was put down in a fresh way that made people select it out of a bombardment of messages and that made people care and respond to it, it was not even going to be perceived.
Before 1949, typically advertising copywriters would write ad copy and then take the text to their art department to lay out the ad. Bernbach’s advertising firm, Doyle Dane Bernbach, combined copywriters and graphic designers into one collaborative creative team that sought to produce ads that were original, fresh, and imaginative. Doyle Dane Bernbach’s ads were prominent drivers of a creative revolution in U.S. advertising.
Competition for attention today has reached a level that Bill Bernbach probably never imagined. A creative revolution in advertising today requires deep changes in business organization and integrating sense in communication across words, images, and personal actions.
The ad that changed advertising
Carl Hahn had contracted his agency, Doyle Dane Bernbach (DDB), to promote a car called the Volkswagen in the United States. Bernbach’s problem was that Hahn’s call came at the end of the fifties, when America was in a deep love affair with stylish vehicles made in Detroit, USA. How could DDB sell a small, ugly, cheap, foreign car that Hitler had a hand in creating to the American public? Luckily for Hahn, Bill Bernbach was the most innovative ad man of his time, being a key player in what is today known as the Creative Revolution.
The campaign that DDB put together for Volkswagen in 1959 would not only make their car “as American as apple pie” but also be recognized by Advertising Age as being the greatest ad of all time and change the industry forever.

4. Contemporary Advertising
Contemporary advertising attracting customers to their product range has become more difficult because consumers have become more literate in technology and, therefore, can research items before purchase. Nowadays remote controls are in the hands of every individual, and the access to hundreds of cable channels means that advertising must generate interest among the viewers. Along with these experiments, there are also new leading edges, such as Internet and social media marketing. In contemporary times advertisers and agencies today see innovations like digital ads and interactive advertising as challenges and opportunities rather than difficulties.
Contemporary advertising are methods of advertising that are basically generic in nature and are widely used. It can be used to build the relationship with the client through market sensing and recognizing categories of clients according to their choice. It also helps to bridge the gap via the use of digital inbound marketing techniques.
The Future of Advertising
Yulia Khansvyarova, Head of Digital Marketing at SEMrush,
“I have no doubts that the future of advertising lies in the digital world. Traditional marketing channels have exhausted themselves and are now stepping back. In my opinion, the future of digital advertising is about personalization, multi-device targeting, and building a unified user-centered ecosystem. Right now such ecosystems are just appearing.
There is a lot of talk about cross-device tracking, mobile ads, and different marketing channels used as a complex. But in reality, if you want to build a system that will be able to keep an eye on user behavior and follow all user steps in decision-making, you will still need to code a lot and build a custom solution yourself. In the nearest future, I guess, this situation will change for the better.”
There’s no question that technology will continue to shape the future of advertising. We’ve already seen dramatic shifts in form and factor, powered by technologies such as 3D, artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and virtual reality. As the landscape continues to change, advertisers that don’t follow suit risk getting left behind.
Artificial intelligence will eliminate the loopholes in the existing digital advertising processes. AI relies on data-driven accumulated information; the AI-based neural networks are capable of experience-based self-learning. This means that with more interaction or repeated application, they evolve to become better and better. To put it into perspective, in the context of advertising, AI can provide the consumer behavior patterns with more precision; it can help create better campaigns by identifying more focused target consumer groups and more.
It is tough to forecast what form advertising will take in the future. But one thing is sure: it will continue to advance and strive to become more useful to business and to the consumer.
B. Importance of Advertising
Introduction
We come across the different types of advertisements in our day-to-day life. In these times of social, economic, and political change, it’s more important than ever to build trust using reputable, respected communications and channels in your marketing. The success of any business, large or small, depends on that business’s ability to market their products and services effectively. Having a great product and great customer service, but if people don’t know your business exists, you are not going to have any sales!
Consumer expectations remain higher than ever when it comes to advertising, or rather, the lack of it. The effectiveness of advertising depends on the assessment of the consumer’s motivation in buying and a direct or indirect appeal to that motivation; sometimes it depends on the creation of that motivation by an appeal to a range of consumers’ natures. Advertisements are of countless importance for any business activity, as they appeal to people to use the particular service.
Now let’s find out why advertising is important for any business.
1. Launch of new product or services
Introducing a new product to the market gives a company the chance to endorse its new offering and encourage its reputation and image at the same time. Launching a new product can be an exciting time for any company. Whether it is the first product the company has offered or an addition to an already existing line, the eagerness is catching the dreams of instant success.
Example:
a. Pingit by Barclays
In 2012, Barclays launched the mobile app Pingit, a mobile payment service that lets users transfer money easily through their mobile phones. Available only for U.K. residents, the service allows users to transfer money to other people using only their phone numbers. Soon after the app was launched, Barclays made the most of its social media buzz to collect real-time user feedback.
b. Chrome by Google (Thailand Launch)
Google wanted to introduce its Chrome browser to a more diverse market by bringing it to Thailand. But launching a product in a diverse market comes with its own challenges, as you need to adapt your strategy according to cultural preferences. Realizing that people in Thailand appreciate traditional storytelling, Google decided to implement that into their product launch campaign.
They chose to tell the story of Ramakien, a national epic that stems from the Hindu story of Ramayana and focuses on the triumph of good over evil. The idea was to use visual storytelling to demonstrate the features of Chrome while bringing the ancient story to life. This helped users understand the browser’s capabilities without having to watch a long, boring tutorial. They even added in-story games so that the audience remained intrigued throughout the interactive experience.
2. Source of income
Advertising revenue is the monetary income that individuals and businesses earn from displaying paid advertisements on their websites, social media channels, or other platforms surrounding their internet-based content. In September 2018, the U.S. Internet advertising market was estimated to be worth $111 billion, with market share being held mostly between Google, Facebook, Amazon, and Microsoft. These companies earn revenue through online advertising but also have initiated pathways for individual users and social media “influencers” to earn an income. Individuals and businesses can earn advertising revenue through advertisement networks such as Google AdSense, YouTube monetization, and others.
3. Advertisement and Sales Promotion
Sales promotion is implemented to attract new customers, to hold present customers, to counteract competition, and to take advantage of opportunities that are revealed by market research. It is made up of activities, both outside and inside activities, to enhance company sales. Outside sales promotion activities include advertising, publicity, public relations activities, and special sales events. Inside sales promotion activities include window displays, product and promotional material displays, and promotional programs such as premium awards and contests.
Sale promotions often come in the form of discounts. Discounts impact the way consumers think and behave when shopping. The type of savings and its location can affect the way consumers view a product and affect their purchase decision. The two most common discounts are price discounts (“on sale items”) and bonus packs (“bulk items”). Price discounts are the reduction of an original sale by a certain percentage, while bonus packs are deals in which the consumer receives more for the original price. Many companies present different forms of discounts in advertisements, hoping to convince consumers to buy their products.
4. Increases sales
Advertising increases the visibility of your brand. This attracts prospects who need your product. Whether you are trying to encourage new customers to buy an existing product or launching a new service, there are many advertising channels to choose from.
It’s important to choose an advertising strategy that suits your business and targets the right audience, and you have to choose the right type of advertising, which will increase sales.
5. Maximizes profit
Advertising is a technique used by firms in monopolistic competition to create product differentiation and gain some control of the market, and as a result, charge a higher price. Excessive advertising will serve to inform consumers about the physical difference in the product, and the perceived difference will lead to increased product differentiation. If advertising convinces customers that the product is superior to the competitor’s, then the firm would charge a higher price
6. Advertisement make aware and educate them.
Advertising helps to make consumers aware of a product and aims to build preference for that product over its competitors. If advertising succeeds in those two tasks, consumers will choose the advertised product when they make their next purchase. Advertising helps to protect consumers against false advertisements, which improves the information consumers can use to make decisions about which products and services to buy.
An advertisement benefits both the seller and the consumer. Sellers can promote their goods through ads. On the other hand, consumers can know the information of goods and discount deals available in the market, so they can make informed decisions.
7. Is Art, Science, and Profession
Is advertising an art or a science? This debate continues to rage endlessly. According to Bill Bernbach, “Advertising is fundamentally persuasion, and persuasion happens to be not a science, but an art.” Advertising is all about the art of persuasion, of selling products and services. An advertiser is a salesperson creating sales for business by making people want to buy things.
“The more creative an ad is, and the better it works, the harder it is to actually pre-test that using conventional methods like question and answer,” Pynta said. “The ads are often indirect, they’re quirky, they’re different, and the traditional sort of methods struggle to capture that.
To succeed in the fast-paced world of today’s marketing, the modern marketer must be multi-dimensional, with multifaceted knowledge ability. Although art and science tend to lean toward different ends of the creative spectrum, the modern marketer must channel both artistry and science. Social media today reported on an infographic by Matt Wesson from Pardot that explains the dual role of the modern marketer.
According to the infographic, marketers today need to find a balance between art and science. In the ever-evolving marketing landscape, the role of the marketer is no longer reliant upon an ad campaign’s level of catchiness. It’s simply not enough. Marketers must harness both the left brain and the right brain to communicate successfully.
Social media today suggests that modern marketers “have a strategic and analytical mind dedicated to measurable metrics but that is always craving a creative outlet.” As the infographic suggests, the modern marketer is one part artist and one part scientist. Create a seamless blend of creativity and analytics, and marketing success is attainable.
8. Element of a marketing mix
The marketing mix consists of four important variables of marketing, or the 4 Ps: Product, Price, Promotion, and Place. Aside from the traditional 4 Ps, there are also other variables like packaging, position, and pace.
9. Persuasion for results
Advertising uses persuasion to make people act in a desired direction.
It pursues people to:
- Purchase (buy) products,
- Subscribe a service,
- Invest in ideas,
- Attend events, and so on.
10. Monitor demand and supply
Advertising spending is one of those ambiguous areas of supply and demand theory where we don’t really know exactly what will happen, but we can make a pretty good guess. Advertising is an effective way to build brand awareness and to tell consumers about the benefits of your product or service.
Creating targeted advertising campaigns can help businesses increase demand for their offerings. But advertising also costs firms money. The distinction we have to keep in mind is whether or not advertising affects the marginal cost of production or whether their advertising budget is fixed. The difference between these two methods decides whether or not to supply the side. However, if an advertising campaign is unsuccessful, it can also reduce the demand for the products or services. It’s important to understand how advertising works and the ways it can change the demand or supply for your product.
11. Build’s brand image
Brand advertising is a form of advertising used to establish connections and build strong, long-term relationships with consumers over time. Companies that use brand advertising aim to get long-term positive recognition by establishing brand identity, credibility, and loyalty and connecting with prospects intellectually and emotionally to motivate them to take action in the future.
For example: BMW

Better customer experiences mean happier customers, and happier customers mean better brand equity! So how do leading brands find that sweet spot with local marketing?
BMW is one of the best examples of a brand doing this right. As one of the most well-known brands in the automotive industry, today BMW is synonymous for car buyers with both refined elegance and blistering performance. Featuring a diverse line of luxury sedans, convertibles, and coupes, BMW offers the very finest in automotive engineering. You’re probably thinking of one or two of their “Ultimate Driving Machine” ads just hearing about it.
But the true piece de resistance for BMW’s brand equity is the customer’s dealership experience. Through powerful local marketing—advertisements, on-premise marketing materials, direct mail campaigns, co-op programs, and more—the organization’s unique values are delivered right to the brand’s customers where they already are. In this article, we’re going to dive right into how BMW makes this all happen to learn how a great brand builds up brand equity through exceptional local marketing.
Source: https://www.campaigndrive.com
12. Target-oriented
Targeted advertising is a form of online advertising that is directed towards audiences with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting. These traits can either be demographic, which are focused on race, economic status, sex, age, level of education, income level, and employment, or they can be psychographic, which are focused on the consumer’s values, personality, attitudes, opinions, lifestyles, and interests. They can also be behavioral variables, such as browser history, purchase history, and other recent activity. Targeted advertising is focused on certain traits, and the consumers who are likely to have a strong preference will receive the message instead of those who have no interest and whose preferences do not match a product’s attribute. This eliminates wastage.
13. Generate employment
Advertising is a type of marketing communication used to promote or sell something—like goods, services, or ideas. Because there are so many steps to creating an advertisement, and given the varied types of jobs in the industry as a whole, there are many advertising job titles and descriptions.
Advertising is usually paid for by sponsors and viewed through various media such as websites, newspapers, magazines, television, radio, outdoor advertising, or direct mail. An advertising firm might create advertising campaigns for various clients or for one company. Advertising gives companies the opportunity to differentiate themselves and highlight their unique selling points.
Advertising increases the sale of goods, which enables the advertisers to produce goods on a large scale. Advertising thus provides employment to a huge number of people and raises their standard of living.
C. Features of Advertising
Introduction
An advertisement is a way of marketing a brand, a product, or a service. Everything needs to be popularized and promoted by way of an advertisement. Hence, understanding advertising is very necessary. Here are some features of advertisements:
1. Advertisement must have paid form
Advertising is an art, and it requires skills. There are advertising companies that offer advertising services to companies and charge them heavily for the services that they provide. However, sometimes companies end up paying billions on an advertising campaign and don’t get effective results in return. Effective advertising is that which generates much more profit than what a company has paid to get the service. Advertising is always a paid form of communication and hence commercial in nature.
2. It is nonpersonal. The person need not be present
Advertising should be impersonal. You can make an ad for a targeted group of people. That does not mean you can direct a message towards an individual through advertising.
For example, if an ad agency of some product, on its own, advertises a brand about a particular product, it will convey to the consumers necessary information regarding that product, but no expenditure has been incurred by the seller for these advertisements.
3. Advertising has to promote goods, services & ideas
It is directed towards increasing the sale of the products and services of a business unit. Advertising is aimed at promoting and selling not only tangible and physical goods but also ideas and services like banking and insurance companies.
4. There must be an identified sponsor
Another feature of advertising is that its sponsor can be identified. Whenever we come across an advertisement, its sponsor is easily identified. Advertising discloses or identifies the source of the opinions and ideas it presents. On the other hand, the sponsor for publicity or propaganda can remain unidentified.
D. Benefits of Advertising
Introduction
According to C.L. Bolling, “Advertising can be described as the art of creating a demand for an article or a service. From the various definitions of advertising mentioned above, the key elements of advertising are:
- It is the non-personal selling of goods or services or ideas to the public in general.
- It carries a message to the customers and reminds them carefully.
- It informs the existing and prospective customers about the quality and utility of the goods or service.
- It builds interest in new products, new technology, new business concerns, etc.
- It is sponsored and paid for.
- It creates awareness regarding the products, etc.
The main benefits of advertising are as under:
Benefits to Manufacturers
- It increases sales volume by creating attraction towards the product.
- It helps with the easy introduction of new products into the markets by the same manufacturer.
- It helps to create an image and reputation not only of the products but also of the producer or advertiser. In this way, it creates goodwill for the manufacturer.
- Retail price and maintenance are also possible by advertising where price appeal is the promotional strategy.
- It helps to establish direct contact between manufacturers and consumers.
- It leads to smoothing the demand of the product. It saves the product from seasonal fluctuations by discovering new and new usages of the product.
- It creates a highly responsive market and thereby quickens the turnover that results in lower inventory.
- Selling cost per unit is reduced because of increased sale volume. Consequently, product overheads are also reduced due to mass production and sale.
- Advertising gives the employees a feeling of pride in their jobs and in being in the service of such a concern of repute. It thus inspires the executives and workers to improve their efficiency.
- Advertising is necessary to meet the competition in the market and to survive.
Benefits to Wholesalers
- Advertisements facilitate easy sale of product; they reduce the selling efforts and the selling expenses of the wholesalers.
- It increases the stock turnover rate of the wholesalers.
- The reputation for a product created by the manufacturer through advertisements is shared by the wholesalers.
- Advertising provides product information to the wholesalers.
Benefits to retailers
- Advertisements reduce the sales efforts and the selling expenses of the retailers, as the consumers are already aware of the availability and the features of the advertised products.
- It contributes to large sales volume.
- It increases the stock turnover rate of the retailers.
- The reputation of the product created by the manufacturer through advertisement is shared by the retailers.
- It enables the retailers to have product information.
- Advertising builds up prestige for the retailers’ shops
- It stabilizes the prices and thereby protects the retailers against any loss resulting from price fluctuations.
- A small retailer cannot afford to employ salesmen for canvassing to get orders. But because of the advertisements placed by the manufacturer, he can get orders easily.
Benefits to salesman
- Introducing the product becomes quite easy and convenient because the manufacturer has already advertised the goods, informing the consumers about the product and its quality.
- Advertising prepares necessary ground for a salesman to begin his work effectively. Hence, sales efforts are reduced.
- The contact established with the customer by a salesman is made permanent through effective advertising because a customer is assured of the quality and price of the product.
- The salesman can weigh the effectiveness of advertising when he makes direct contact with the consumers.
Benefits to consumers
- An advertisement brings the new products to the notice of the consumers and helps them satisfy their wants.
- It raises the standard of living of the consumers by stimulating their desire for a variety of new products.
- It provides protection against deception, because advertised products are, generally, of good quality.
- It saves time, effort, and money for the consumers in obtaining information about the product.
- Advertisements contribute to the reduction in the selling prices of goods for the consumers by encouraging increased sales and production.
- By providing information about the relative merits of the various goods available in the market, advertising helps the consumer in intelligent buying.
- Prices of advertised goods are known to the consumers. As such, the consumers can get the goods at the advertised retail prices and protect themselves against the higher prices that may be charged by the dealers.
- Modern advertisement is highly informative. Through it, the consumers can know the varied uses of the products.
Benefits to society
- Advertising, in general, is educative in nature.
- Advertising leads to large-scale production, creating more employment opportunities for the public in various jobs directly or indirectly.
- It initiates a process of creating more wants and their satisfaction, a higher standard of living. For example, advertising has made more popular and universal the uses of such inventions as the automobile, radio, and various household appliances.
- Newspapers would not have become so popular and so cheap if there had been no advertisements. The cheap production of newspapers is possible only through the publication of advertisements in them. It sustains the press.
- It assures employment opportunities for the professional men and artists.
- Advertising does provide a glimpse of a country’s way of life. It is, in fact, a running commentary on the way of living and the behavior of the people and is also an indicator of some of the future in this regard.
E. Limitation of advertising
The following are the main limitations of advertising:
1. Less Forceful
Absence of personal touch makes advertising less forceful. Paying attention to the message is not compulsory for the customers. For example, jewelry advertisements do not give a personal touch to male viewers.
2. Lack of Feedback
It is very difficult to judge the effectiveness of an advertising message, as there is no accurate feedback regarding its impact. For example, in times of political surveys, respondents are not clear about the political parties, their agenda, or work, and sometimes the biased nature of respondents also limits the feedback.
3. Inflexibility
Advertising messages are standardized and hence cannot be changed according to the requirements of different customers. This is a limitation of advertising because society is divided into a number of segments like demographic, geographic, psychographic, etc. However, the market is diversified by large different viewers; hence, one particular product advertisement targets a limited specific group. For example, baby diaper advertisements (Pampers, Huggies, etc.) are mainly targeted to newborn babies.
4. Low Effectiveness
An increase in the volume of advertising has made it difficult to make any advertising message in general be received properly by the target customers. Many messages don’t really get even noticed, not to speak of being effective, etc. For example, on the TV channel or on the road in India, there are more advertisements than content, which is irritating and distracting us, and we look for advertisement-free channels.
F. Effects of Advertising
The image of definite, attractive, unique, memorable, and encouraging advertisements has all the time had a deep impact on the society, be it positive or negative. So, if an advertisement is positive and has good principles, it helps to better the society we exist in. However, on the other hand, if an advertisement is ambiguous or undesirable, it strongly affects the society in a negative manner. So, there are thousands of advertisements produced every year, and most of them disappear with a certain impact, intentionally or unintentionally, in the minds of the public.
There are many advertisements that have a positive impact on the minds of people, such as the advertisement promotion of “TATA Tea” with its tagline “jaago re,” which is significantly cheering to the public, as it has a positive communication to “awaken” the people of India in the direction of their real aims and duties. P&G advertisement promotion also has a positive impact on the society, as it donates a piece of the sales earned to an NGO named “Shiksha.”

This advertising campaign inculcates a sense of awareness and care among the masses. Even the advertisement campaigns of certain financial firms serve to be helpful to the society, as they make the public aware of how certain significant and useful financial matters work. Such advertisement campaigns include that of LIC, Manappuram Gold Loan, bank advertisements, SEBI, etc.
Thus, there are a variety of such advertisements that have a positive impact on the society we live in and are therefore advantageous as well. However, there is a greatly more shady and grave side of this field, which is a serious matter of concern. While there are definite advertisements that have a positive outcome on the society, there are many more advertisements that have a very negative impact on the society and drag it towards the wrong direction.
For example, the Center Fruit advertisement shows that, immediately by considering the name of the product, one’s tongue starts lisping and goes out of control. Another example of such overstatement is the recent 5 Star advertisement campaign, which shows that, on eating the chocolate, due to its flimsiness, one gets lost into the world of his own…!! Also, in the Fevistick ad campaign, they show that whatever thing can be joined by using the product, just anything, and that too in no time! Even if the coin given for change while buying the Fevistick is kept on the product, it gets fixed to it! In Happydent White’s advertisement, one’s teeth start shining the moment he/she chews the product, and then the teeth can serve as an alternative to tube lights…!!
There are a variety of such advertisements that show an extremely overstated use of the product/service to be marketed. Due to such advertisements, even if the public knows the real usefulness of the product, they will go and buy the product. Looking at the nationwide point of view, this is a total waste of resources. In a way, it is fooling the public to sell the products.
The major aim of approximately all firms to sell their products is the youth. Thus, nearly all advertisements made today are youth-centered. While making the advertisements, they comprise certain matter that no doubt attracts the youth but is frequently harmful for them and others. For example, advertisements of Thums Up, Mountain Dew, Bajaj Pulsar, etc., show a convincing deadly stunt, which increases the “cool quotient” of the product. Though there is a small mark of disclaimer at the underside of the screen while the advertisement is broadcasted, the youth jumps to copy the stunts, and the penalty of such actions may be deadly. So, the youth tries to copy the stunts shown in the advertisements in pleasure, and then insensitive penalties follow.

Thus, various advertisements direct attention to the social evils that are well-known in the nation. The most horrible example is the treatment of women. The way women are projected in the advertisements today has led to certain terrible stereotypes. They are just kept to grab the interest of the public in the direction of the product. Nowadays, instead of giving sufficient information about the product, the makers choose to keep women for the sake of attainment of attention.
If women are offended in the society today, much of it is due to such advertisements! Just for the sake of exceeding the sales, the dignity of a gender is put at risk. You must have seen all the advertisements for “AXE” deodorants. It is the most awful example of how women are used to give the wrong impression to the public towards the product to be sold. There are many more such examples of advertisements, like those of Set Wet, Engagement Deodorants, Wild Stone, Fair and Handsome, Gillette, Mahindra Centro Bike, etc., which project women just as a symbol of seduction to draw more customers in the direction of the product.
Thus, the advertisements mainly influence the society both positively and negatively, and also the society affects the advertisements being made in the country, up to a convinced extent. However, as accountable to citizens of India, we should feel free to convey our thoughts against any such advertisement that we find deceptive or unwanted and try to recover the condition of our society with little but with the best we can do! Anyways, we can never run away from this outcome of advertisements. We will remain on altering the advertisements they make and will keep on changing us.
CRITICISM OF ADVERTISING
Introduction
The shaping of the most frequent criticism of advertising depends on who is doing the criticizing. Advertisers complain about the high cost to advertise. Consumers criticize ambiguous claims and products that don’t live up to their advertising. Advertising has been criticized as long as it has existed. Several objections have been raised to advertising, and some people criticize advertising as a social waste. The following is the criticism of advertising:
1. Elevated Price: It is said that large amounts used up on advertising raise the cost of distribution, which is transferred to customers in the form of higher prices. This disagreement may be true in the case of inelastic demand, when advertising just transfers demand from one producer to another. But efficient advertising frequently creates demand and increases the level of production. Large-scale operations result in lower costs and lower prices. In developed countries, businessmen have condensed costs and prices while spending millions on advertising every year.
2. Uneconomical Consumption: Advertising increases the needs of people and encourages harmful consumption. By exploiting human sentiments, it persuades people to buy products that they do not need or cannot have enough money to buy. Advertising promotes artificial living and wastefulness and creates demand for unimportant goods. This claim may be true to some level, but it is based on the statement that satisfaction of psychological needs is not as significant as that of physiological needs. Moreover, new tastes and better emotional experiences of life are necessary for the growth of civilization. By itself, advertising cannot force people to buy things that they consider needless.
3. Misleads the Consumer: It is said that advertising is frequently misleading and misrepresents facts to the consumer. Overstated and elaborate languages are used to fool innocent consumers. They are induced or defrauded through fake testimonials and false comparisons to buy goods of doubtful value. There is no denying the detail that some firms spoil in false and misleading advertising, and dishonest use of advertising by them destroys public confidence in advertising. But just because a few people use wrong advertising, it does not mean that advertising itself is bad or unnecessary.
4. Creates domination: Advertising creates brand preferences and restricts open competition. Large firms, which can pay for huge amounts of money on advertising, remove small firms by creating brand domination. Advertising thus encourages the continued existence of the mightiest rather than the best. But promotion creates only a temporary brand monopoly, as after some time other brands offer competition. For instance, the ‘Amul’ brand of butter enjoys domination of the brand but has to face competition from Vita, Neutralite, Go, and other brands of butter.
5. Wastage of National Resources: In order to make use of advertising, producers create unimportant differences in their products. The expensive resources that can be used to create new industries are exhausted in the production of needless varieties and designs. Appearance, design, and style have become more significant than the physical usefulness of the product. Manipulative and aggressive advertising leads to criminal wastage of resources.
6. Undermines Social Values: Advertisement is a kind of daydreaming for the people. These days it is pleasing the people away from actuality and into the kingdom of artificiality. Through its medium, people get information about new products.
7. Confuses the Buyers: Many a time a twisted description of reality is shown in the advertising. Believing in advertising, consumers buy the product. They come to understand later that the information given in the advertisement was something else, whereas the actual product was quite different from it. On its use, they feel cheated.
8. Encourages Sale of Inferior Products: Every company projects its product as the greater one in the advertisement. Therefore, the buyer is incapable of deciding as to which product is actually good. It affects other sellers also. Therefore, it is said that advertisement encourages the sale of low-grade products.
9. Some Advertisement Is in Bad Taste: Many times, unclean language and unpleasant pictures are used in advertising in order to be a focus for a particular class. They may be offensive to a particular class. It causes decay of social values.
10. Annoyances and Cautions: Other criticisms of advertising are that most of it is ridiculous or abusive and often entices people to buy things they don’t need or want. What’s ridiculous or abusive to one person, however, may be funny or heading for to another. So before running an advertisement, advertisers sometimes rely on focus groups to give their impartial opinions.
G. 5M’s of advertising
Introduction
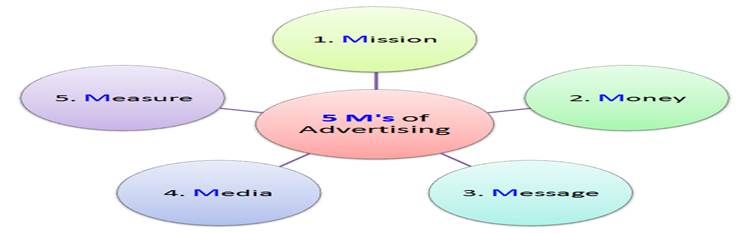
The five M’s of advertising are described by Philip Kotler in his book Marketing Management, Eleventh Edition (Prentice Hall). Advertising is any paid form of non-personal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor.
In developing an advertising program, always start with identifying the target market and the buyer’s motives. Advertising is one of the most popular and powerful tools of market promotion. It involves several decisions. Some experts explain advertising decisions and activities in the form of five ‘M’s as under: mission, money, message, media, and measurement.
1. The first ‘M’ stands for Mission – Advertising Objectives
Advertising objectives can be classified as to whether their aim is:
To inform: This aim of advertising is generally true during the pioneering stage of a product category, where the objective is building a primary demand.
This may include:
- Telling the market about a new product.
- Suggesting new uses for a product.
- Informing the market of a price change.
- Informing how the product works.
- Describing available services.
- Correcting false impressions.
- Reducing buyers’ fears.
- Building a company image
To persuade: Most advertisements are made with the aim of persuasion. Such advertisements aim at building a selective brand.
To remind: Such advertisements are highly effective in the maturity stage of the product. The aim is to keep the consumer thinking about the product.
2. The second ‘M’ stands for Money – Advertising Budget
As time is important in the advertisement, how can you ignore your budget? Money is also a critical decision while going for advertisement.
Different media charge different costs. The Internet is cheap media to advertise, but everyone cannot use the Internet in his advertisement strategy.
TV is a more costly but effective medium for advertisements. Most of the companies reserve media budgets separately.
Every type of media has different package for advertisements; for example, newspapers have so many packages for advertisements, and TV channels also have different budget packages according to time
3. The third ‘M’ stands for Message – Creating Advertising Message and Copy
Message generation can be done in the following ways:
Inductive: By talking to consumers, dealers, experts, and competitors. Consumers are the major source of good ideas. Their feeling about the product, its strengths, and weaknesses gives enough information that could aid the message generation process.
Deductive: John C. Meloney proposed a framework for generating advertising messages.
According to him, a buyer expects four types of rewards from a product:
- Rational
- Sensory
- Social
- Ego Satisfaction.
Buyers might visualize these rewards from:
- Results-of-use Experience
- Product-in-use Experience
- Incidental-to-use Experience
4. The fourth ‘M’ stands for Media—Advertising Media Selection and Media Scheduling
Definitely, the selection of media is the most important component in the advertisement. There are so many media available for advertisement, but selection is at the same time so much more critical.
The decision of media selection depends on the target market because the organization will first analyze how its target market gets information about the organization, whether they are connected to the internet or through traditional media like the newspaper.
Use of media is also critical because of the money budget and time budget. Different media charge different costs at different times.
It is the promotional manager’s duty to study which time is effective with which media.
5. The fifth ‘M’ stands for Measurement—Measuring and Evaluating Advertising Effectiveness (MEAE)
Evaluating the effectiveness of the Advertisement Program is very important, as it helps prevent further wastage of money and helps make corrections that are important for further advertisement campaigns. Researching the effectiveness of the advertisement is the most used method of evaluating the effectiveness of the Advertisement Program. Research can be in the form of:
- Communication-Effect Research
- Sales-Effect Research





